Min troligen tråkigaste födelsedag… Så närmar man sig 40 år, bara 2 år kvar. Blir dock inte deprimerad, men känner ibland att jag är så värdelös… Men har gått i KBT, o man ska inte tänka så.
Torsdag 17 maj, 2018
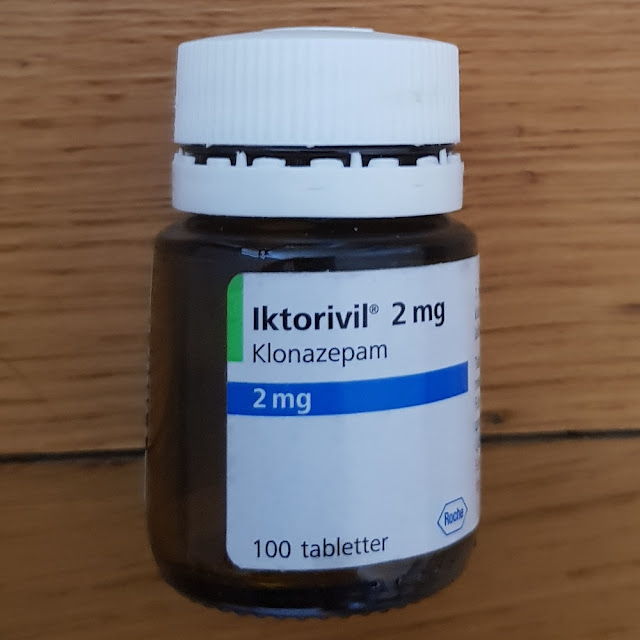
Var hos psykiatern idag. Han gick med på mitt förslag om att byta ut en del av Iktorivilen mot Lyrica. O nu skriver jag detta i efterhand, så har det gått jättebra. Har halverat Iktorivilen, en veckas abstinens, men sen gav det med sig. Lyrica, 75 mg x 2 st per dag. Lyrica ger en annan form av lugn. Har som mål att bli av med alla lugnande, kanske bara att ha vid behov.
Har ju ätit bensodiazepiner i ca 17 år o då blir man kraftigt beroende. Men jag ska med hjälp av Lyrica klara av detta! Det finns en risk att man kan bli beroende av Lyrica också, men jag ska försöka att inte bli det.
Mår dock bra på 300 mg Venlafaxin, ska säga det till psykiatern när han ringer mig, att jag gått ner med 75 mg. Han skrev dock ut av misstag enorma mängder Venlafaxin…
Onsdag 9 maj – Lördag 12 maj, 2018
Nu återupptar jag bloggen.
Inga kvitton mer!
9:e till 12:e maj var jag med gruppen inom konstprojektet i Skellefteå. Det var jättekul. Men jag o de andra blev väldigt rädda när planet landade i Skellefteå, de bakre landningsställen tog inte i samtidigt, o planet vickade rejält. Jag hann bli riktigt rädd att vingen skulle ta i marken.
Vi träffade gängen från Hallsberg, Botkyrka o Skellefteå.
Vi ställde ut våra verk på konstavdelningen på mässan Nordsken, på Skellefteå Kraft Arena. Givetvis fick vi VIP-kort. Annat var mycket cosplay o utklädda till fantasy-personer. Jag trivdes väldigt bra. Sömnen fungerade, vilket jag alltid är rädd för när jag reser bort.
Pappa var med på att köpa den nya utgåvan av ett Super Nintendo, med 21 inbyggda spel. Så jag minns klassikerna som vi spelade på 90-talet.
När vi flög hem fick vi dock vänta ca 6 timmar på byte på Arlanda.
Som sagt, det hela var mycket trevligt!
Fredag 04 maj, 2018
Onsdag 2 a maj, 2018
Tisdag 1 maj, 2018
Måndag 30 april, 2018
Söndag 29 april, 2018
Lördag 28 april, 2018
Fredag 27 april, 2018
Boendestödet kom 09:30, vi gick o handlade.
Tog sedan 11:18-tåget till Helsingborg.
Jag och pappa snackade o höll på med datorerna, o jag fick en dator, en Acer i-5, men det är fel på den. Den stänger av sig själv efter några minuter. Ska lämna in den o se om det är nått att reparera.
Sen gick vi hem till Kenneth och Lena, träffade Elins fina hundar. Kl 19 var vi på teater och såg ”Figaros Bröllop”, den var bra. Ett par öl efter det.
Sen var jag lite orolig att gå ensam runt 23:30-tiden från teatern, till Knutpunkten, bärandes på en dator. Tog bort säkringen från min spray o hade den i handen hela tiden. Lite orolig för gäng i form av kolsäckar… Nattmat på McDonalds.


















Kommentarer